The History of Medicare
President Lyndon B. Johnson enacted a Medicare bill In 1965, enabling individuals aged 65 and over to access healthcare coverage through a nationwide program. Initially, the available coverage options were limited to Part A and Part B.
Over time, the coverage has undergone significant developments and expansions, encompassing a larger population compared to its early years.
Presently, more than 60 million individuals benefit from Medicare coverage. While Part A and Part B generally cover the majority of expenses, there are supplementary policies regulated by the federal government that can be purchased to address any gaps not fully covered by Original Medicare.
Parts Of Medicare
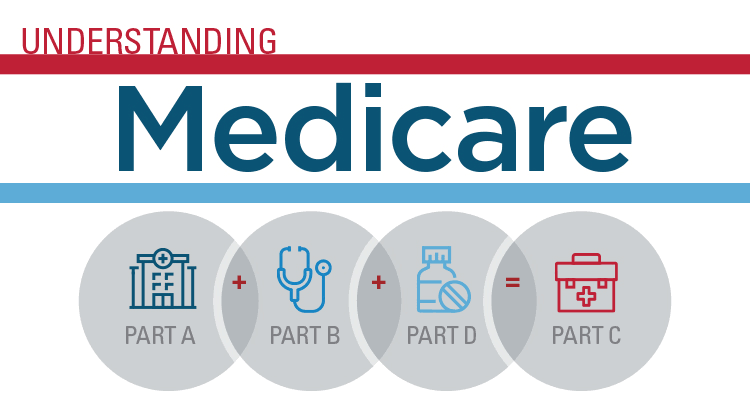
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A provides hospital insurance that assists individuals with the expenses related to inpatient care and stays at skilled nursing facilities. It also offers coverage for services like hospice care and home health care. In essence, Part A can be considered as Medicare’s provision for room and board expenses during a hospital stay.
Part A covers the cost of a semi-private room. However, it does not encompass all the treatments that may take place in a hospital or clinical setting, such as outpatient surgeries. These types of treatments would typically fall under Part B.
For most individuals aged 65, the cost of Part A is $0. This is because, throughout their working years, they have contributed taxes to pre-fund the premiums for their hospital benefits. Alternatively, one can also obtain Part A at no cost through their spouse or ex-spouse’s work history. Even if automatic eligibility for premium-free coverage is not met, most individuals aged 65 can still acquire it, albeit at a substantial premium cost.
What is Medicare Part B?
Medicare Part B is the coverage provided for outpatient medical services. It encompasses all medical services that are not included in your inpatient hospital care. Without Part B, you would not have insurance for doctor’s visits, including those within the hospital. Additionally, Medicare coverage for lab work, preventive services, ambulance services, and outpatient surgeries would not be available.
It is crucial to note that Part B also covers cancer therapy and kidney dialysis, which are highly expensive treatments. Without Part B and supplemental coverage, these treatments would be financially burdensome.
The cost of Part B is determined by Social Security and is subject to change annually. Individuals with higher incomes are required to pay more than those with lower incomes. Your Part B premium is based on your modified adjusted gross income, which is reported to the IRS.
What is Medicare Part C?
Medicare Part C, also known as the Medicare Advantage program, is a private insurance option. The cost of Advantage plans can vary depending on the carrier, county of residence, and the specific plan chosen.
In order to enroll in a Part C plan, you must first be enrolled in both Parts A and B of Medicare. Even if you find a Part C plan with a low premium, you will still need to pay for Part B. Additionally, you must reside in the service area of the plan and apply during a valid election period.
Once you are enrolled, your Medicare coverage will be provided by the Advantage plan itself, rather than the government.
The reason why you don’t enroll in Part C at Social Security is because it is a voluntary program. Many individuals prefer to receive their Medicare coverage through Original Medicare and traditional Medigap plans. These individuals do not wish to have a Part C Advantage plan, so they simply choose not to enroll in one.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to opt for a Part C plan or stick with Original Medicare A & B and enroll in Medigap, along with a Part D plan, is up to you and your budget.
What is Medicare Part D?
Medicare Part D, the latest addition to our national health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and above, provides coverage for prescription medicines. Prior to 2006, there was no Medicare coverage for outpatient drugs. However, with the introduction of Part D, millions of Medicare beneficiaries enrolled to receive coverage for their prescription medications.
Part D covers retail prescription drugs that can be obtained either by visiting a pharmacy or through mail order. To sign up for a Part D drug plan, you need to select a carrier and enroll in their plan. Most states offer around 30 different drug plans to choose from. To determine the most suitable plan for you, it is recommended to have your agent conduct a Part D analysis using Medicare’s prescription drug finder tool.
What is Medicare vs Medicaid?
Many individuals often wonder about the distinctions between Medicare and Medicaid (Medi-Cal). Medicare is a health insurance program specifically designed for senior citizens, while Medicaid is a form of financial and healthcare aid for low-income individuals. It is worth noting that some individuals who are 65 years old or older may be eligible for both programs. In such cases, Medicare takes precedence as the primary insurance, while Medicaid acts as the secondary coverage.

The government offers various Savings Programs that can be accessed through your state’s Medicaid office. These programs can potentially assist you in paying your Part B premiums and provide support for your prescription drug plans. To determine if you qualify for these programs, it is advisable to consult with your state’s Medicaid office.
What doesn’t Medicare cover?
This question is quite significant as numerous individuals are uninformed that it fails to encompass all the healthcare expenses that beneficiaries may come across.
Medicare excludes coverage for:
– Long-term care
– Hearing aids
– Regular dental care
– Routine vision care
– Medical care outside of the United States
– Dentures
– Plastic and/or cosmetic surgery
– Massage therapy.
Takeaways
1. The Medicare program consists of four distinct parts, namely Part A, B, C, and D. It is important to note that Part C, D, and Medigap plans are offered by private insurance carriers (such as Medicare Advantage Plans) rather than the federal government.
2. Upon enrolling in Medicare Part A and Part B, individuals are presented with two primary plan choices. They can either opt for a Medigap plan and a Part D plan, or they can choose to enroll in an Advantage plan.
 Mario Arce
Mario Arce
Mario A Arce is an accredited and liscensed Medicare Health Insurance Adviser. He has been working with medicare clients since 2016. Serving California members in San Bernardino & Riverside county.
Producer CA Lic.#0L10564
Contact me.

